Understanding Arthritis
Arthritis is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide, causing pain, inflammation, and stiffness in the joints. There are several types of arthritis, each with its own set of symptoms and treatment options. This article will provide an overview of rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and other types, along with insights into common symptoms, treatments, and what you can do to manage this condition.
Common Causes of Arthritis
Several factors can contribute to the development of arthritis, including:
Muscle or ligament strain
Bulging or ruptured discs
Arthritis
Skeletal irregularities
Osteoporosis
Poor posture
Obesity
Stress and tension
Autoimmune disorders
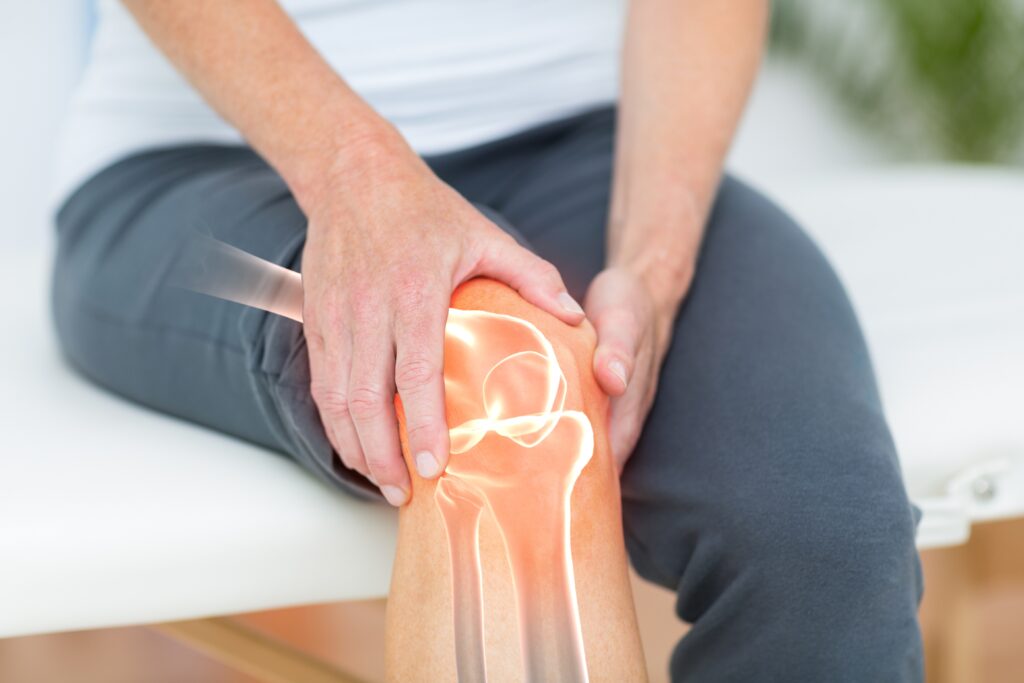
Symptoms of Arthritis
Symptoms of arthritis vary depending on the type, but the most frequent symptoms include:
Joint Pain: Persistent pain in affected joints, which may worsen with activity
Stiffness: Joint stiffness, especially in the morning or after sitting for extended periods
Swelling: Inflammation and swelling around the joints
Redness and Warmth: The skin over the affected joints may appear red and feel warm to the touch
Decreased Range of Motion: Reduced ability to move the joint through its full range of motion
Fatigue: General tiredness or a feeling of being unwell
Grating Sensation: A grinding sensation in the joint during movement
Bone Spurs: Extra bone growths may develop around the affected joints
Diagnosing Arthritis
Arthritis diagnosis typically involves several steps to accurately identify the type and extent of the condition. Here’s an overview of the process:
Medical History: The doctor will ask about symptoms, duration, and any family history of arthritis or autoimmune diseases. Key symptoms include joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and reduced range of motion
Physical Examination: The doctor will examine the affected joints for swelling, redness, warmth, and range of motion. They may also assess any other areas of the body that may be affected
Laboratory Tests: These can help identify inflammation and check for specific markers associated with various types of arthritis, such as rheumatoid factor (RF), anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPA), and antinuclear antibodies (ANA). Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP) tests may be used to assess inflammation levels in the body
Imaging Tests:
X-rays: These can help visualise joint damage, bone spurs, or changes in joint structure
MRI or Ultrasound: These imaging techniques can provide detailed images of the joints and soft tissues, helping to identify inflammation or damage that may not be visible on X-rays.
Joint Aspiration: In some cases, a doctor may use a needle to withdraw fluid from a swollen joint for analysis. This can help rule out infections and assess for crystals, which can indicate gout or pseudogout
Diagnosis of Specific Types: Based on the findings from the above steps, the doctor may diagnose specific types of arthritis, such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, gout, or psoriatic arthritis, among others
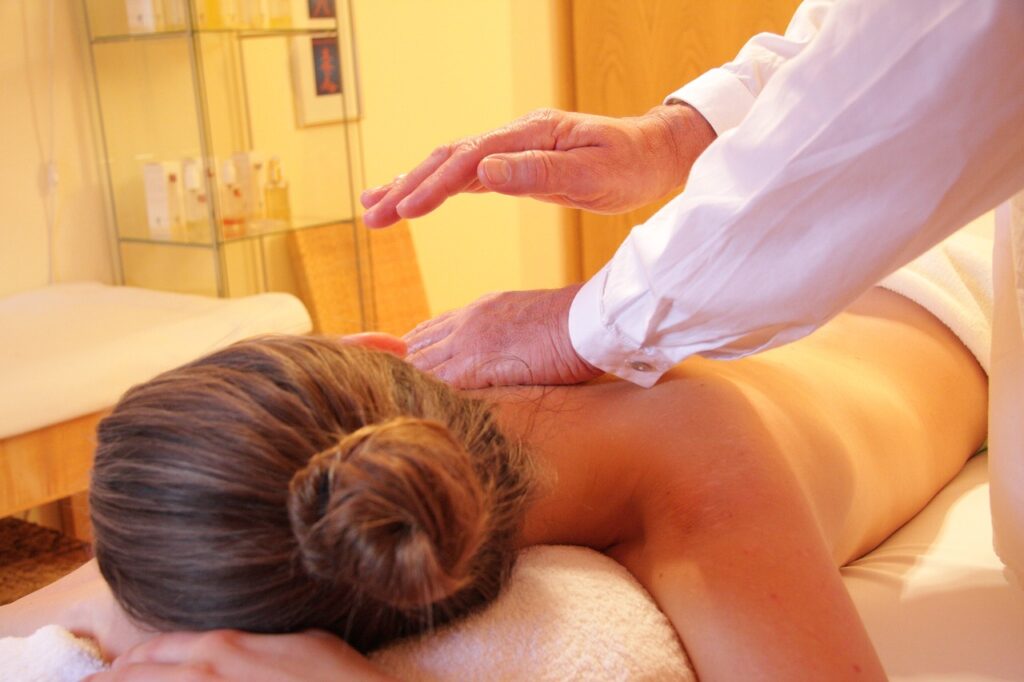

Treatment for Arthritis
There are various approaches to treating arthritis, depending on its severity and underlying cause:
Home Remedies
Heat and cold therapies
Epsom salt bath
Over-the-counter pain relievers
Exercise and physical therapy
Dietary Changes
Professional Treatments
Osteopathy: Osteopathic treatment can be highly effective for arthritis. Osteopathy can provide pain relief and improved mobility using the following techniques:
Soft tissue manipulation
Joint mobilisation
Spinal manipulation
Myofascial release
Muscle energy techniques
Cold laser therapy
Dry needling
Physiotherapy: A physiotherapist can provide:
Tailored exercise programs and therapy
Pain management
Education
Massage Therapy: Remedial massage can help:
Relax tense muscles
Improve circulation
Increased range of motion
Lymphatic drainage
Acupuncture: This traditional Chinese medicine technique may help alleviate arthritis pain.
Medications: Your doctor may prescribe:
NSAIDs
Corticosteroids
Anti-inflammatory drugs
Surgery: In rare cases, severe arthritis may require surgical intervention such as joint replacement or repair.
Preventing Arthritis
While it may not be possible to completely prevent arthritis, there are several lifestyle changes and strategies that can help reduce the risk of developing certain types of arthritis and manage existing symptoms. Here are some effective prevention tip:
Maintain a healthy weight
Exercise regularly, focusing on core strength
Eat a balanced diet
Stay hydrated
Protect your joints and avoid repetitive stress
When to Seek Professional Help
If your arthritis symptoms or pain are severe, persistent, or interfering with your daily activities, it's time to consult a healthcare professional. At Inner West Osteopathy, our experienced osteopaths take great care in treating arthritis pain and mobility issues using a holistic approach that addresses the root cause of your discomfort.
Don't let the pain of arthritis control your life. Contact us today to schedule an appointment and take the first step towards a pain-free future.





