Understanding Bursitis
Bursitis is a common condition that causes pain, swelling, and discomfort in the joints. It occurs when the small, fluid-filled sacs called bursae, which cushion the joints, become inflamed. There are several types of bursitis, each with its own symptoms and treatment options. Common forms include shoulder bursitis, hip bursitis, and knee bursitis. Understanding the typical symptoms and available treatments can help you take the necessary steps to manage bursitis effectively and improve your joint health.
Common Causes of Bursitis
Several factors can contribute to bursitis, including:
Repetitive motion
Prolonged pressure
Injury or trauma
Overuse
Infection
Underlying conditions
Age-related wear
Symptoms of Bursitis
Common symptoms of bursitis can vary in severity, but the most frequent signs include:
Pain: The primary symptom, often sharp and intense, especially with movement or pressure
Swelling: The affected area may become visibly swollen due to fluid buildup in the bursa
Tenderness: The area around the inflamed bursa is sensitive to touch
Limited Range of Motion: Pain may restrict movement in the affected joint, such as the shoulder, elbow, or knee
Redness or Warmth: The skin around the area might be red and feel warm to the touch (in cases of infection or severe inflammation)
Stiffness: The joint may feel stiff or difficult to move, especially after periods of rest
Diagnosing Bursitis
Bursitis is commonly diagnosed through the following methods:
Medical history and physical examination: A doctor will ask about your symptoms, recent activities, and any history of joint problems. They will then examine the affected area for signs of swelling, tenderness, and reduced range of motion
Imaging tests: X-rays, while not able to show bursae, can help rule out other conditions such as fractures or arthritis. Ultrasound is often used to detect inflammation in the bursa and surrounding tissues, and in some cases, an MRI may be utilized to provide more detailed images of soft tissues to confirm bursitis
Aspiration: If infection is suspected, a doctor may insert a needle into the affected bursa to withdraw fluid for laboratory analysis (called aspiration) to check for infection or gout
Blood tests: Blood tests might be done to rule out other conditions like infection or autoimmune diseases
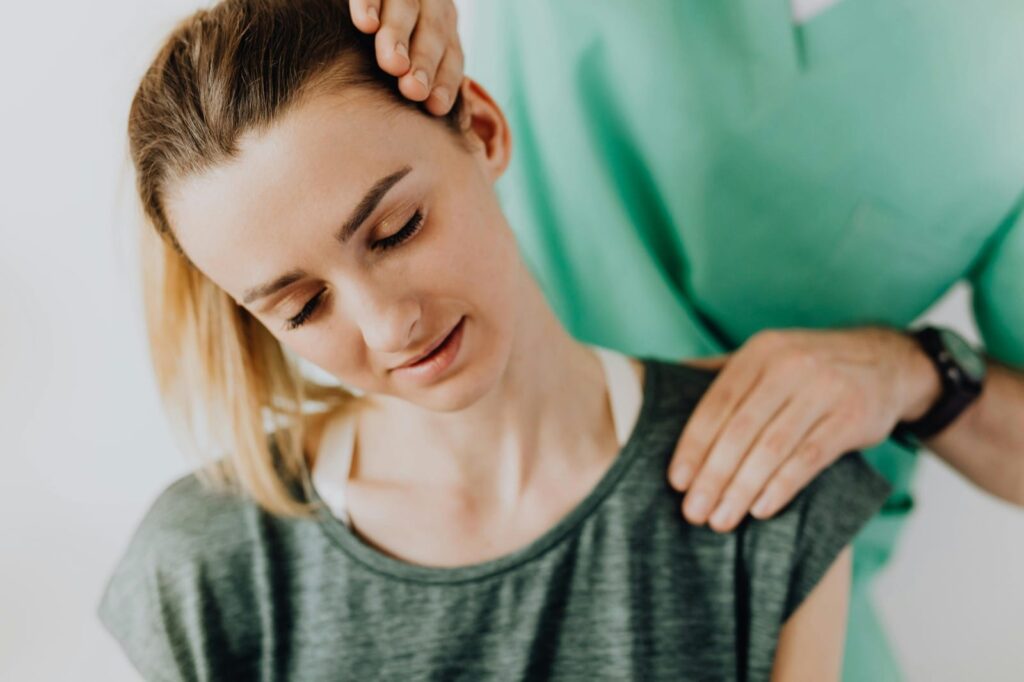

Treatment for Bursitis
There are various approaches to treating bursitis, depending on its severity and underlying cause:
Home Remedies
Rest the affected area
Ice Therapy applied the affected area
Over-the-counter pain relievers
Compression bandaging
Elevate the affected area
Professional Treatments
Osteopathy: Osteopathy can be an effective approach to treating bursitis by focusing on relieving pain, reducing inflammation, and improving joint mobility using the following techniques:
Soft tissue manipulation
Joint mobilisation
Posture and Alignment Correction
Lymphatic Drainage Techniques
Physiotherapy: A physiotherapist can provide:
Tailored exercise programs and therapy
Pain management
Education
Massage Therapy: Remedial massage can be beneficial for treating bursitis by addressing the muscle tension and inflammation surrounding the affected joint. While massage therapy doesn’t directly treat the inflamed bursa, it can alleviate symptoms and prevent further irritation. Here's how remedial massage helps with bursitis:
Relieving Muscle Tension
Improve circulation
Increased range of motion
Cold Laser Therapy: Cold laser therapy (also known as low-level laser therapy or phototherapy) can help treat bursitis by:
Reducing inflammation in the affected bursa
Accelerating soft tissue repair at the cellular level
Providing pain relief through disruption of pain receptors
Stimulating cellular repair through enhanced mitochondrial function
Improving blood flow to the affected area
Dry Needling: This technique can be effective for bursitis by targeting myofascial trigger points around the affected joint:
Releases muscle tension that may be contributing to joint stress
Improves range of motion in the surrounding tissues
Reduces pain through neuromuscular response
Helps normalise muscle function around the affected bursa
Can be particularly effective when combined with other manual therapy approaches
Acupuncture: This traditional Chinese medicine technique may help alleviate bursitis pain.
Medications: Your doctor may prescribe:
NSAIDs
Corticosteroids
Muscle Relaxants
Topical Analgesics
Antibiotics
Surgery: In rare cases, severe bursitis may require surgical intervention such as removal of the bursa or damaged tissue surrounding it.
Preventing Bursitis
By incorporating these preventive measures, you can help reduce your risk of developing bursitis and maintain healthier joints:
Avoid pepetitive motions
Use proper body mechanics
Wear proper footwear
Use cushioned surfaces when kneeling or sitting for long periods
Mantain a healthy weight
Warm up and cool down when exercising
When to Seek Professional Help
If your bursitis symptoms—such as pain, swelling, or limited range of motion—are severe, persistent, or interfering with your daily activities, it's important to consult a healthcare professional. At Inner West Osteopathy, our experienced osteopaths are dedicated to treating bursitis with a holistic approach that addresses the root cause of your discomfort.
Don’t let the pain of bursitis dictate your life. Contact us today to schedule an appointment and take the first step toward a pain-free future.





